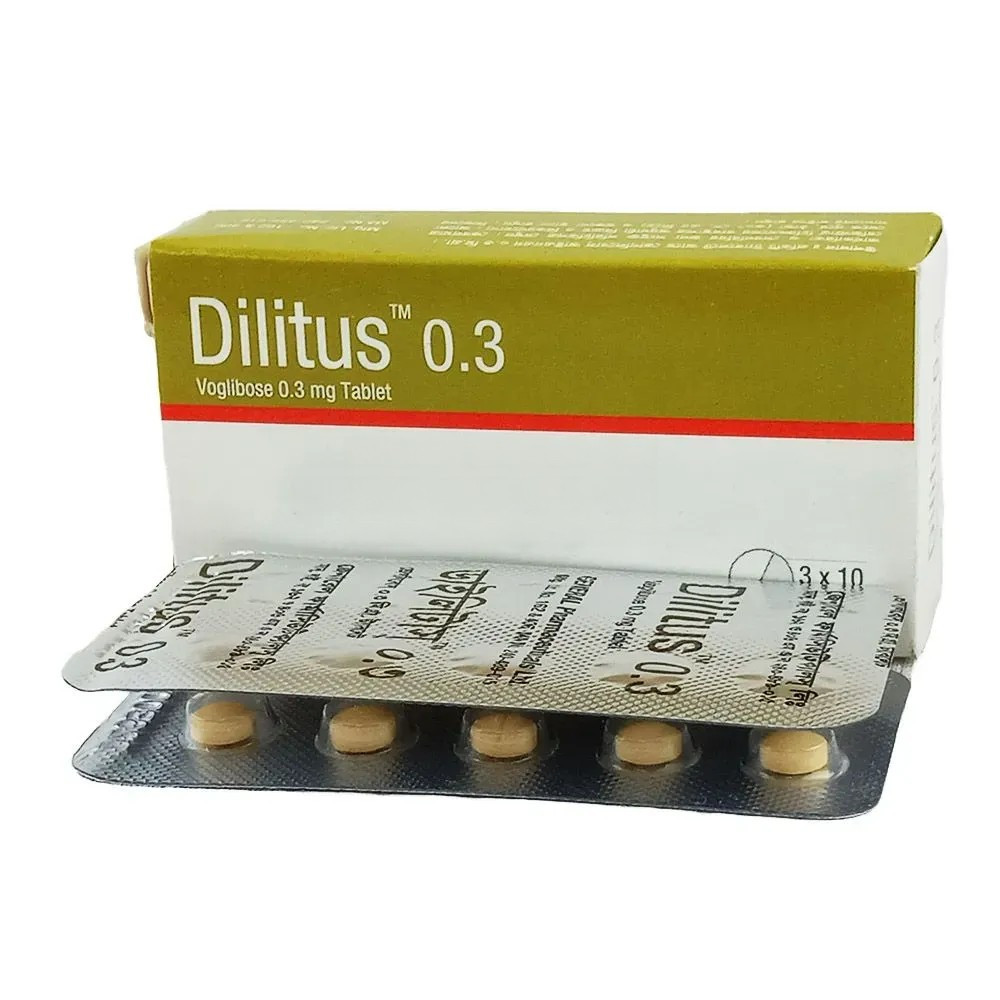

Dilitus Tablet, Voglibose 0.3 mg
Inhouse product
-
৳11.40
৳12.00 -
৳42.75
৳45.00 -
৳16.63
৳17.50 -
৳2.14
৳2.25
Reviews & Ratings
Indications
Dilitus is an
alpha-glucosidase inhibitor & indicated-
- in non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients as immunotherapy
- in combination with other oral
hypoglycaemic agents
- in addition to insulin in
diabetes mellitus patients
- in prevention of onset of type
2 diabetes mellitus in impaired glucose tolerance
- in elderly patients and in
those with hepatic dysfunction or mild to moderate renal impairments in
whom other oral hypoglycaemic agents are contraindicated or they need to
be used with caution, it will be helpful.
- in glycogen storage disease: It
is helpful in prevention of hypoglycaemia in patients with type lb
glycogen storage disease.
- in non-diabetic
hyperinsulinemia, it is helpful in preventing hypoglycaemic attacks.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Pharmacology
Alpha-glucosidase
inhibitors are saccharides that act as competitive inhibitors of enzymes needed
to digest carbohydrates: specifically alpha-glucosidase enzymes in the brush
border of the small intestines. The membrane-bound intestinal
alpha-glucosidases hydrolyze oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and
disaccharides to glucose and other monosaccharides in the small intestine. Acarbose
also blocks pancreatic alpha-amylase in addition to inhibiting membrane-bound
alpha-glucosidases. Pancreatic alpha-amylase hydrolyzes complex starches to
oligosaccharides in the lumen of the small intestine. Inhibition of these
enzyme systems reduces the rate of digestion of complex carbohydrates. Less
glucose is absorbed because the carbohydrates are not broken down into glucose
molecules. In diabetic patients, the short-term effect of these drugs therapies
is to decrease current blood glucose levels: the long term effect is a small
reduction in hemoglobin-A1c level.
Dosage & Administration
Adult Dose: Usually, Voglibose tablets are orally
administered in a single dose of 0.2 mg, 3 times a day, before each meal. If
the effect is not sufficient, the quantity of a single dose may be increased up
to 0.3 mg.
Paediatrics: The safety and effectiveness of Voglibose in
children has not been established.
Geriatrics: Since elderly patients generally have a
physiological hypofunction, it is desirable that such caution should be taken
as starting the administration at a lower dose (e.g. 0.1 mg at a time). Furthermore,
this drug should be carefully administered under close observation, through the
course of the disease condition, with careful attention to the blood sugar
level and the onset of gastrointestinal symptoms.
Dosage in Renal
Failure: Voglibose is poorly
absorbed after oral doses and renal excretion is negligible, suggesting that no
dose adjustment is required. However, pharmacokinetic studies in patients with
renal insufficiency are not available.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
Dilitus should be
administered with care when co-administered with the following drugs:
Antidiabetic drugs- Derivative(s) of sulfonylamide and sulfonylurea, biguanide
derivatives, insulin preparations and improving agents for insulin resistance.
For the concomitant use of anti-diabetic drugs and the drugs which enhance or
diminish the hypoglycaemic action of antidiabetic drugs:
- Drugs enhancing the
hypoglycaemic action of antidiabetic drugs: β-blockers, salicylic acid
preparations, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, fibrate derivatives, warfarin,
etc.
- Drugs diminishing the
hypoglycaemic action of antidiabetic drugs: Adrenaline, adrenocortical
hormone, thyroid hormone etc.
Contraindications
Contraindicated in
patients with Hypersensitivity to Voglibose or to any of the excipients;
Diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic pre-coma, severe infection, before and after
operation or with serious trauma; gastrointestinal obstruction or predisposed
to it.
Side Effects
Dilitus unlikely to
produce hypoglycaemia in overdose, but abdominal discomfort and diarrhea may
occur. Moreover loose stools, abdominal pain, constipation, loss of appetite,
urge to vomit (nausea), vomiting, heartburn, increased gas, and intestinal
obstruction like symptoms due to increased intestinal gas may cause. Oral
hypoglycaemic agents plus Dilitus may cause hypoglycaemia (0.1% to <5%),
delay in digestion and absorption of disaccharides, fulminant hepatitis,
serious liver dysfunction with increased liver enzymes, jaundice, anemia,
numbness, edema, blurred vision, hot flushes, malaise, weakness, hyperkalemia,
increased pancreatic enzyme (serum amylase).
Pregnancy & Lactation
The safety of
Voglibose in pregnancy has not been established. However, no adequate and well
controlled studies have been found on pregnant women. Although the levels of
Voglibose reached in human milk are exceedingly low, it is recommended that
Voglibose may not be administered to such women.
Precautions & Warnings
The administration of
Dilitus tablets should be limited to patients who have established diabetes as
there are certain other disease conditions such as abnormal glucose tolerance
and positive urinary sugar that represent diabetes-like symptoms (renal glycosuria,
senile abnormal glucose tolerance, abnormal thyroid function, etc.) In patients
who are being managed with lifestyle modifications (diet and/or exercise),
Dilitus must be given only when the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose levels
are ≥200 mg/dL. During administration of Dilitus, disease progression should be
closely observed with monitoring of blood glucose levels at regular intervals.
If the effect on postprandial glucose levels is not satisfactory even after the
administration of Dilitus for 2 to 3 months (postprandial glucose ≥200mg/dL),
consider a change to more appropriate treatment. After administration of
Dilitus, if sufficient control of blood glucose is achieved (postprandial
glucose ≤160 mg/dL) and can satisfactorily be maintained with lifestyle therapy
or with additional use of oral hypoglycaemic drugs or insulin preparations, the
administration of Dilitus tablet should be discontinued, and subsequent
progresses of disease should be monitored.
Overdose Effects
Unlike sulfonylureas
or insulin, an overdose of Dilitus tablets will not result in hypoglycaemia. An
overdose may result is transient increase in flatulence, diarrhoea and
abdominal discomfort. Because of lack of extra-intestinal effects soon with
Dilitus, no serious systemic reactions are expected in the event of an
overdose.
Therapeutic Class
Alpha-Glucosidase
inhibitor
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool (below
30°C) and dry place, away from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
Frequently Bought Products
Braintel Syrup 100 ml bottle, Brahmi Rasayan
Benzenod Capsule, Rivastigmine Tartrate 3 mg
Fexo Tablet, Fexofenadine Hydrochloride 60 mg
Cipro-A IV Infusion 100 ml bottle, Ciprofloxacin 200 mg/100 ml
Sepnil Solution Chlorhexidine Gluconate + Cetrimide 1.5%+15%
Product Queries (0)
Login Or Registerto submit your questions to seller
Other Questions
No none asked to seller yet
-
৳11.40
৳12.00 -
৳42.75
৳45.00 -
৳16.63
৳17.50 -
৳2.14
৳2.25